TECHNOLOGY
FDM 3D Printing
Fused Deposition Modeling
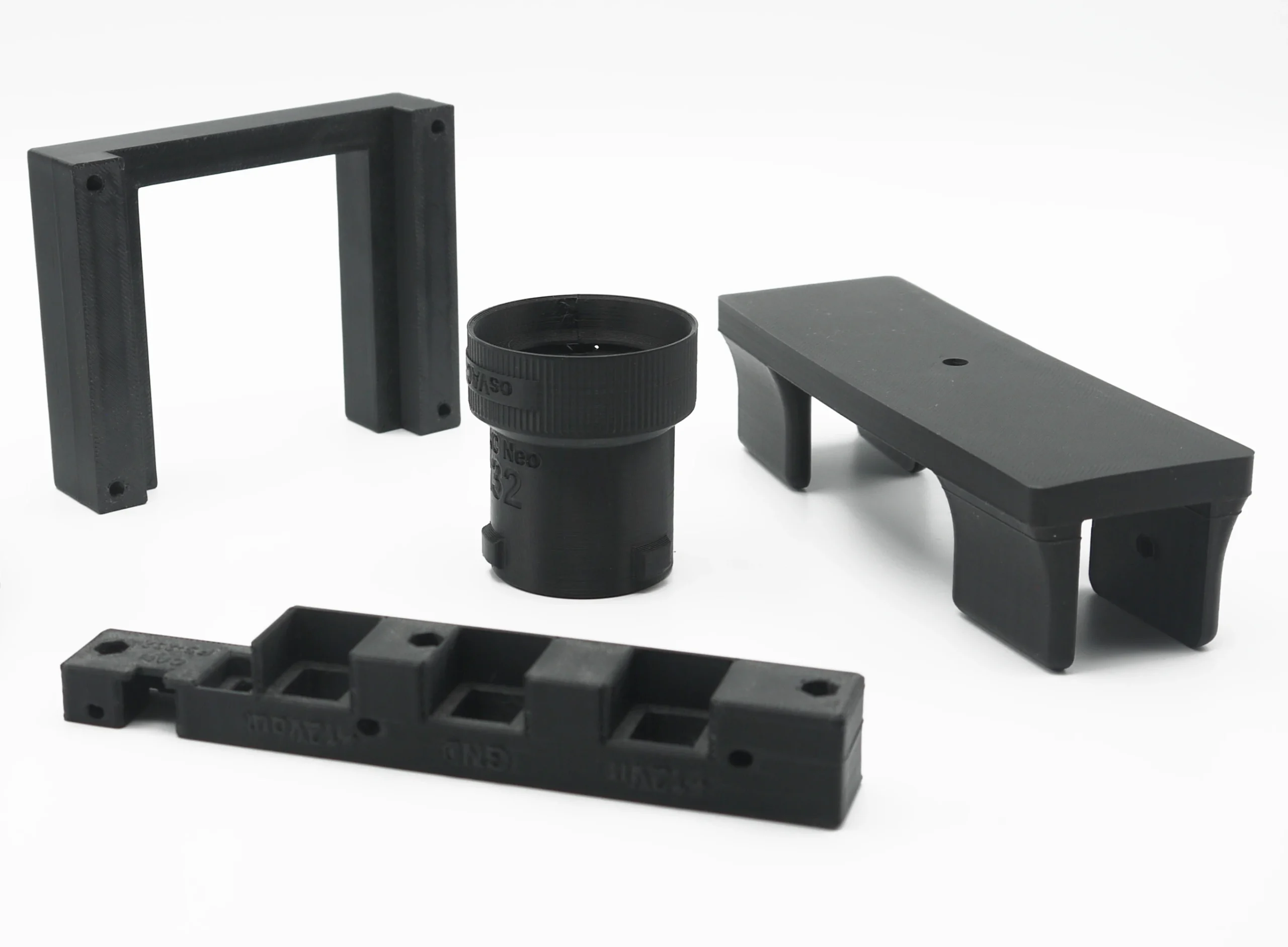
Technique suitable for basic proof-of-concept models, as well as parts that may undergo secondary machining processes. Widely used in architecture, automotive, assembly lines, tooling, decorative applications, souvenirs, etc.
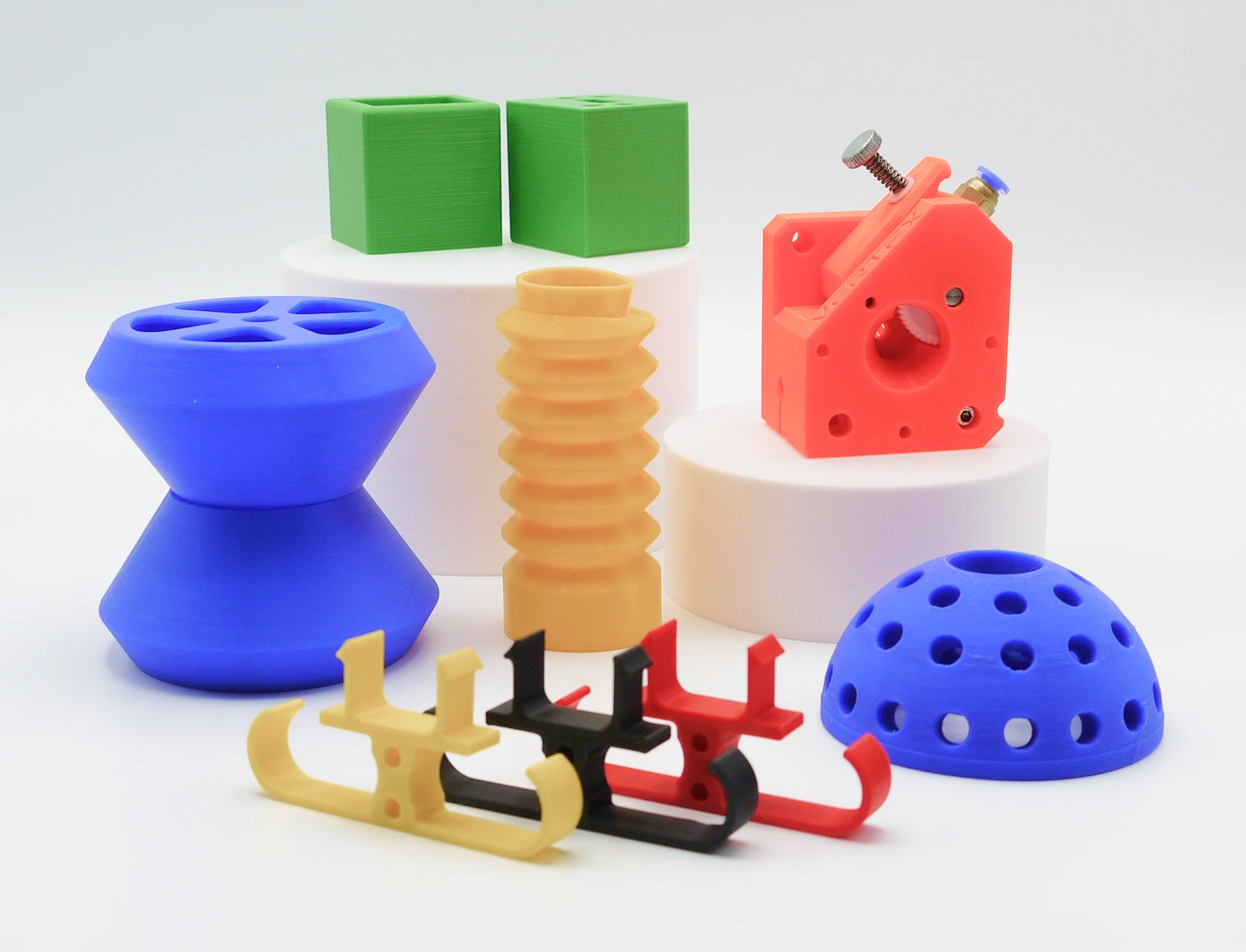
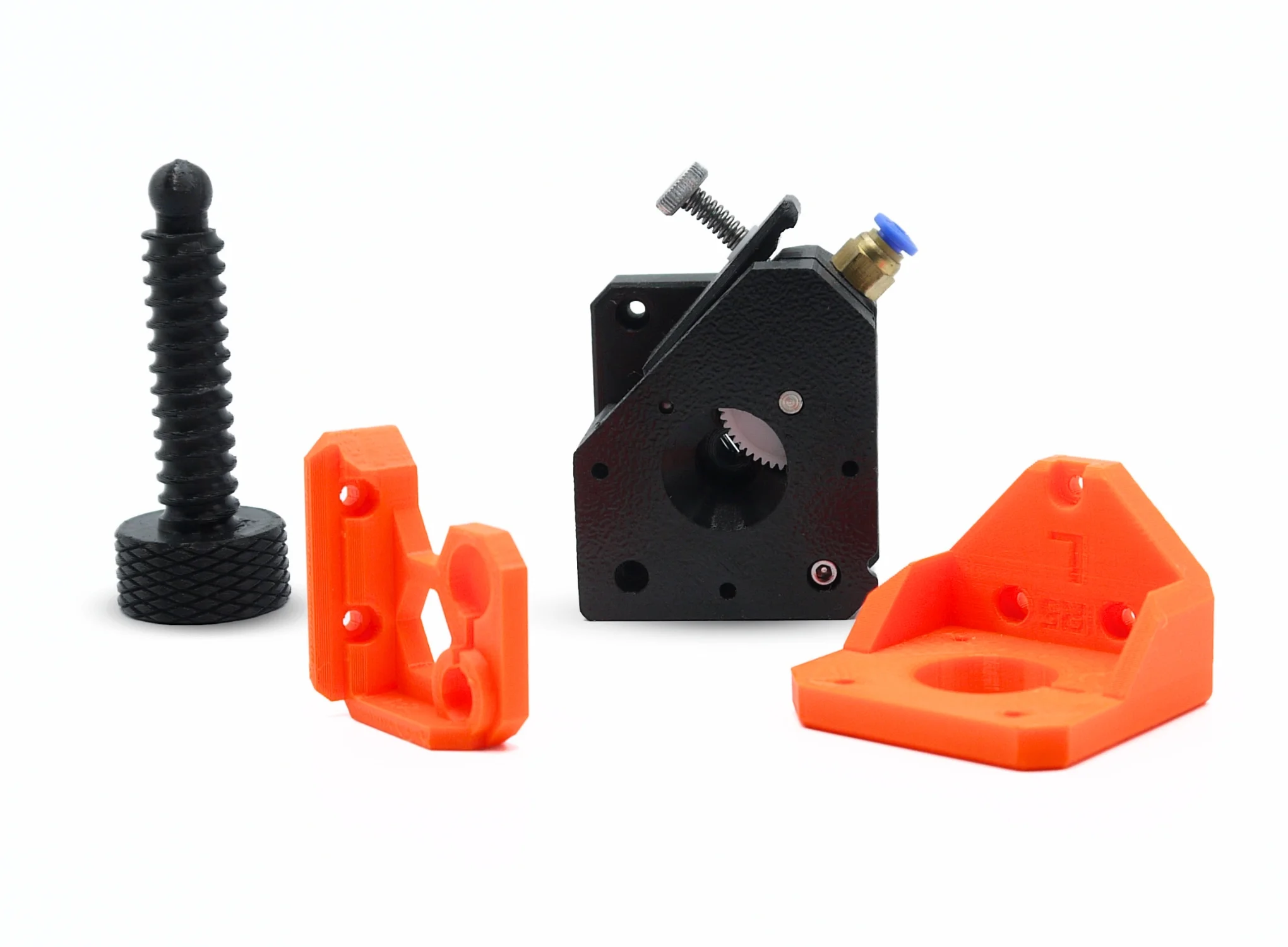


What is FDM 3D Printing?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is one of the most popular 3D printing technologies due to its wide variety of materials, capability to print large-scale parts, and cost-effective accessibility. This technique is ideal for rapid prototyping and low-volume production, offering economical solutions for sectors such as architecture, automotive, tooling, and more. FDM printed parts generally require minimal post-processing, facilitating rapid implementation across different applications.
Minimum Design Tolerances
PARAMETER
VALUE
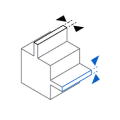
0.2 mm
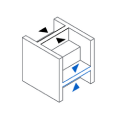
0.2 mm
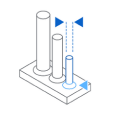
3.0 mm
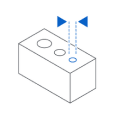
2.0 mm
0.15 mm
0.05 mm hasta 0.55mm
MATERIALS
Wide Selection of Materials for FDM 3D Printing

ABS
ABS is a highly durable, industrial thermoplastic that is both strong and cost-effective. It is perfect for producing functional prototypes, tools, and end-use parts that require impact resistance.
Properties:
-
- Impact-resistant and durable
- Suitable for functional prototypes and industrial parts
- Up to 80% of the strength of injection-molded ABS
- Available in multiple colors
- Impact-resistant and durable
ASA
ASA is ideal for production parts that will be exposed outdoors, as it offers UV resistance and long-term durability.
Properties:
-
- Weather- and UV-resistant
- Strong and tough for industrial applications
- Available in multiple colors
PETG
PETG combines the advantages of ABS, such as strength and durability, with the safety of being non-toxic. It is excellent for applications requiring contact with food or chemicals.
Properties:
-
- Impact- and chemical-resistant
- Versatile and durable
- Available in multiple colors
PLA
PLA is a biodegradable material, ideal for conceptual models and low-cost functional parts. Made from renewable resources, it is perfect for projects with a sustainable approach.
Properties:
-
- Rigid and compostable
- Ideal for aesthetic prototypes and concept models
- Available in multiple colors
TPU
TPU is a flexible polymer with high impact resistance and durability, ideal for parts that require flexibility, such as seals or dampers.
Properties:
-
- Flexible and impact-resistant
- Highly durable with vibration-damping properties
- Available in multiple colors
GreenTec Pro
GreenTec Pro is a high-performance biopolymer that rivals engineering plastics like PEEK. It’s ideal for functional parts requiring strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability.
Properties:
-
- High structural rigidity
- Excellent dimensional accuracy
- Heat and load resistance
- Made from 100% renewable raw materials
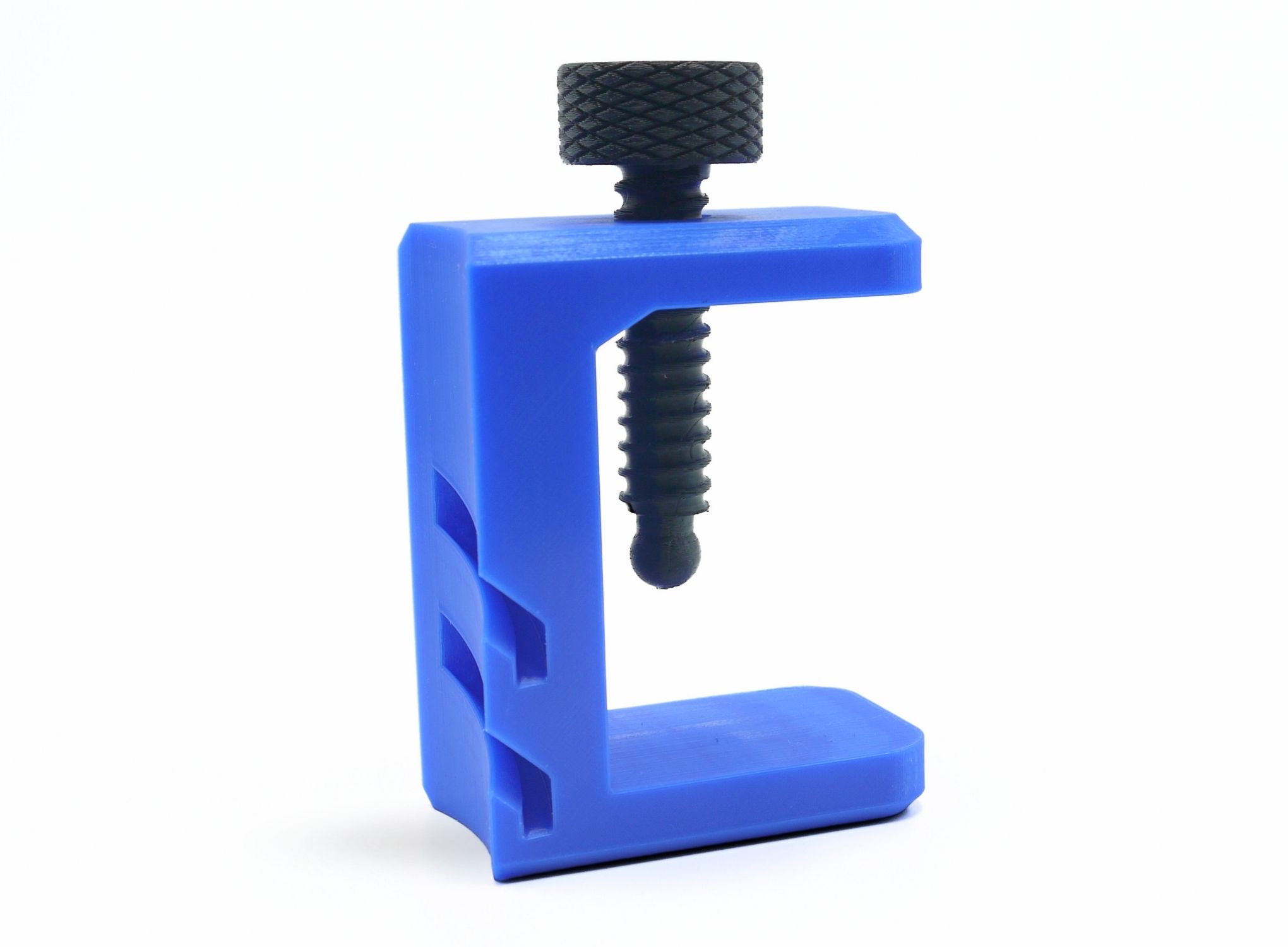

Looking for a fast way to manufacture parts?
With our FDM technology, you can get high-quality functional parts quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively for your project.
MANUFACTURING SERVICES
Discover Our Technologies
At Manfacter, we offer professional-quality 3D printing solutions to bring your ideas to life. From rapid prototyping to end-use parts production, we guarantee high-quality, fast, and cost-effective results. We use industry-leading technologies such as SLS, FDM, SLA, and MJF, allowing us to adapt to the needs of any sector.

It offers speed and the ability to produce complex geometries without support structures.

It offers the highest resolution level and accuracy among all additive manufacturing technologies.

Ideal for engineering thanks to its ability to produce complex geometries.

It offers a wide variety of materials and the capability to produce large parts.

It offers speed and the ability to produce complex geometries without support structures.

It offers the highest resolution level and accuracy among all additive manufacturing technologies.

Ideal for engineering thanks to its ability to produce complex geometries.

It offers a wide variety of materials and the capability to produce large parts.
Frequently Asked Questions About FDM 3D Printing
How does FDM differ from other 3D printing technologies?
Unlike SLA or SLS, FDM is more accessible and affordable, making it ideal for prototypes and quick-use functional parts. Although its precision is lower than SLA, it allows for the production of durable parts with materials such as ABS, PLA, and other thermoplastics.
Is it safe to use FDM parts in functional applications?
Yes, many FDM-printed parts are functional and can be used in low- to medium-stress applications. However, it is important to choose the right material to ensure durability and resistance under specific conditions.
What types of parts are ideal for FDM 3D printing?
FDM is ideal for functional prototypes, quick-use parts, housings, brackets, tools, and low-cost components that require basic mechanical strength. It is widely used in design, engineering, and the production of replacement or customized parts.
Is it possible to manufacture end-use parts with FDM?
Yes, FDM technology is used to produce end-use parts, especially for short runs or customized components. However, it is not always ideal for parts requiring very tight tolerances or extremely smooth finishes without additional post-processing.
What are the design recommendations for FDM 3D printing?
It is recommended to design with wall thicknesses of at least 0.8 mm and to avoid extreme overhangs without supports, as these could affect the quality of the part. Layer orientations should be considered to improve strength in functional applications.
What type of file should I provide for FDM printing?
STL and STEP files are the most common formats for FDM printing. These files retain the geometry of the part and are compatible with most slicing software and FDM printers. You can upload these files to the platform to get an instant quote.
What finishes are available for FDM-printed parts?
FDM parts can be sanded, painted, or even coated to improve appearance and strength. In addition, some materials can be smoothed using vapor treatments to achieve a finer surface finish.
What level of accuracy and resolution can be achieved with FDM?
FDM technology offers an accuracy of ±0.1 mm, with layer heights typically ranging from 50 to 300 microns. The resolution is sufficient for functional parts, although not always suitable for extremely fine details compared to technologies such as SLA.
Does FDM printing require post-processing?
Yes, post-processing may include support removal, sanding, and in some cases finishing treatments such as painting or vapor smoothing to improve the surface. This helps achieve an enhanced visual finish and additional strength.
What maintenance do FDM parts require for long-term applications?
FDM parts can deform over time if exposed to high temperatures or prolonged stress. The type of material has a major impact on durability; for example, ABS is more heat-resistant than PLA and may be better suited for demanding applications.













